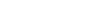Every second counts when someone suffers a cardiac arrest, and while early CPR is vital, a functioning defibrillator can dramatically improve survival chances.
A common question is whether these lifesaving devices need their own power source. So, do defibrillators have batteries?
The short answer is yes; they are the lifeline that keeps these lifesaving devices ready to act when it matters most.
Research analysing AED malfunction reports found that battery and power issues contributed to roughly 23 % of failures, highlighting the importance of reliable batteries in emergencies.
Understanding your AED battery, from its expected lifespan and the correct type for your device to proper maintenance practices, is essential to keep your defibrillator ready to perform in an emergency.
We’ll cover everything you need to know about defibrillator batteries to ensure your AED is always rescue-ready below.
How Long Do Defibrillator Batteries Last?
In practice, most defibrillator batteries are designed to provide standby power for between about 2 and 5 years, depending on the model and manufacturer.
Some specialised batteries, such as the Defibtech Lifeline 7 Year Battery Pack, even deliver up to 7 years of standby life when installed and maintained properly.
This long-lasting performance ensures your AED can operate continuously, but regular checks and timely replacement are still essential to ensure it works in an emergency.

What Type of Battery is In a Defibrillator?
The battery inside your defibrillator is its lifeline. While the exact type depends on your device’s make and model, defibrillator batteries typically fall into three main categories.
Integrated Battery Packs
Many modern AEDs use purpose-built battery packs that combine multiple cells into a single unit. These packs make replacements quicker and easier, and deliver reliable, consistent power for self-tests and emergency shocks.
Most models use non-rechargeable lithium-ion battery packs, providing long standby life without the need for frequent maintenance.
Rechargeable Batteries
A smaller number of professional AED models use rechargeable batteries, though this is not common in the majority of public access models.
Some high-end or clinical AED models are designed to work with rechargeable batteries, usually lithium-ion or nickel-metal hydride. These are ideal for settings where the device may be used frequently or needs to remain powered for extended periods.
While they can be recharged multiple times, they must be properly maintained and charged according to the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure consistent performance and reliability in an emergency.
Pad-Paks
Certain AEDs, such as the HeartSine Samaritan, use Pad-Paks, which merge the battery and electrode pads into a single unit. This design simplifies maintenance by allowing you to replace both the pads and the battery at the same time, reducing the risk of missing or expired components.
Pad-Paks also help ensure that the correct battery and pads are always paired, eliminating compatibility issues. They are available in adult and pediatric versions, making it easy to switch for different patients.
The integrated design also makes tracking expiration dates simpler, helping keep your AED fully ready for use.
Risks of Installing the Wrong AED Battery
It’s important to remember that not all batteries are interchangeable. Each AED model is designed to work with a specific type of battery, tailored to provide the right voltage, capacity and performance.
Incorrect batteries may cause the AED to fail self-tests, deliver insufficient shocks, or stop working entirely in an emergency. They can also damage the device or void the manufacturer’s warranty, leaving you without support if a fault occurs.
To ensure your AED is always ready to save a life, always use batteries recommended by the manufacturer. Investing in the correct battery guarantees that your AED will perform reliably when it matters most.
Keeping Your AED Battery in Top Condition
Even with the right battery installed, it’s important to understand common issues that can affect AED performance.
Being prepared for these scenarios ensures your device remains reliable during an emergency.
Recognise Low Battery Signals
AEDs are designed to alert you when their battery is running low. This might appear as a beeping sound, a flashing light, or a warning on the status display.
When you notice these alerts, replace the battery promptly following the manufacturer’s instructions. Keep spare batteries nearby to ensure your AED is always ready.

Check for Corrosion
Battery contacts can occasionally corrode over time, especially if the AED is exposed to moisture or stored incorrectly.
If corrosion is present, remove the battery and gently clean the compartment with a soft, dry cloth before inserting a new one. Avoid water or cleaning solutions and check that the battery is seated correctly when replaced.
If corrosion is severe or the battery appears damaged, replace it immediately and consult the manufacturer’s instructions.
Prevent Unexpected Drainage
Batteries may lose power faster than expected if the AED is stored in extreme temperatures, high humidity, or direct sunlight.
Regular inspections and careful storage can help extend battery life and prevent sudden failures.
Replace Expired Batteries
All AED batteries have a finite lifespan, usually 2–5 years, depending on the model.
Regularly checking expiry dates and keeping replacements to hand ensures your AED is always ready to deliver lifesaving power.
How We Can Help
At Defib World, we know that a defibrillator is only effective if its battery is reliable.
That’s why we supply a wide range of replacement batteries and battery packs for many AED models, so your device is always ready to perform in an emergency.
We can guide you on choosing the correct battery for your AED and offer advice on maintaining it to extend its lifespan and reliability.
Call us on 0330 223 6336 or email sales@defibworld.org, and we’ll help keep your AED powered and rescue-ready at all times.





























































.jpg)